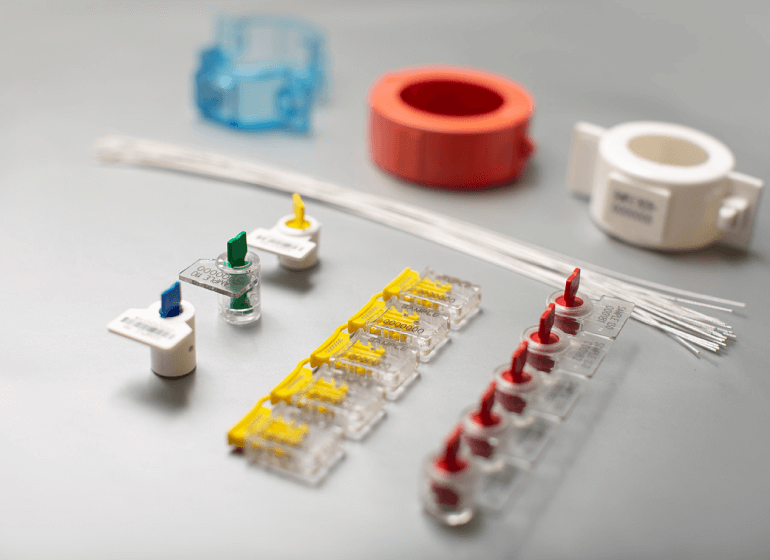
What are Meter Seals? Meter seals are designed to prevent unauthorized access to meters. Meter seals cannot be opened without being damaged, thus it is understood whether they have been tampered with by unauthorized persons.
In which areas are meter seals used?
Meter Seals are primarily used for:
- Electricity, water, and gas meters
- Road transportation
- Fuel transportation

Meter Seals Tampering Methods and Tamper Prevention
Meter seals can be tampered with in any of the following ways:
- Imitation of seals or parts of seals
- Forced entry and post-entry repair
- Careful manipulation of the seal
The following precautions can prevent the tampering with of meter seals:
To add an extra layer of security company logos, company names, unique serial numbers, and associated barcodes are written on the meter seals using a variety of marking methods. Descriptive information such as lot numbers, serial numbers, and barcodes written on the seal provide product traceability to the user, allowing the user to easily identify evidence of tampering, and intervene. These identifying marks can of course be imitated. Here, the proper recording of such identifying marks can prevent the use of fake seals.
The inner parts of some meter seals can be broken during unauthorized entry and reassembled using inner parts taken from another seal. Gökerplast Meter Seals however, are designed to prevent the internal part from being broken and reused without damaging the body.
GP110 Twist Seal: After the inner part is mounted inside the body, it is fixed by mounting the plug on the body. In order to remove the inner part from the body, inteference with the plug is necessary. Since the plug is embedded in the body and joined to the body by ultrasonic welding, it breaks if intefered with, thus providing evidence of tampering. The structure of this seal does not allow the inner part to be removed from the seal without damage.

*Ultrasonic welding method: A welding process that bonds surfaces through high frequency vibration and light pressure.
GP125 Anchor Seal: Anchor seals provide locking by passing the wire through the holes in both the body and anchor parts once the anchor is inserted into the body. Barbs prevent the anchor from being removed with evidence of tampering. To provide further security, the serial number is written on both the seal body and on the anchor.

GP130 Twist Seal: The insert is welded to the body using a hot sealing method. The design does not allow the insert to be removed from the body without leaving evidence of tampering.

GP140 Combi Seal: A security seal with a double-stage locking system and one-piece body. In addition to the locking mechanism of twist seals, the GP140 combi seal has a second locking mechanism, and anchor (see GP125 Anchor Seal). After locking of the twist seal element is achieved, the anchor is inserted, preventing any rotational movement of the first insert. It is not possible to interfere with the internal parts without damaging the seal body, thus it is not possible to reassemble the seal using internal parts taken from another seal. As with the GP125 and GP130, forcing the inserts will result in damage and evidence of tampering.

Source
[1]-Wikipedia.‘Security seal’. Access: 06.04.2022. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Security_seal